Restrictive Lung Disease Flow Volume Loop
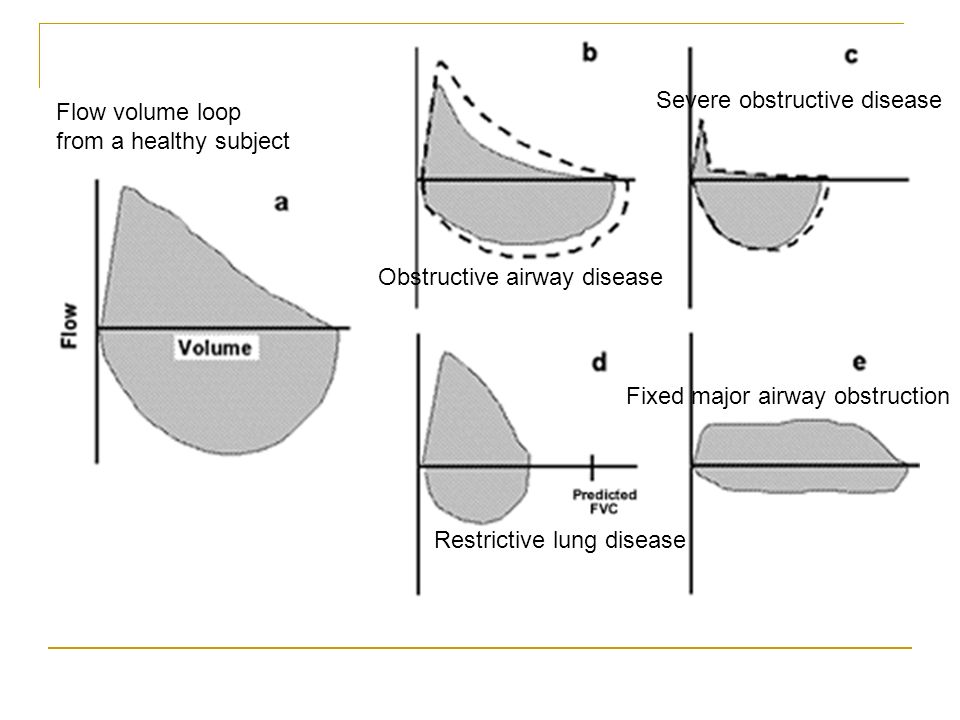
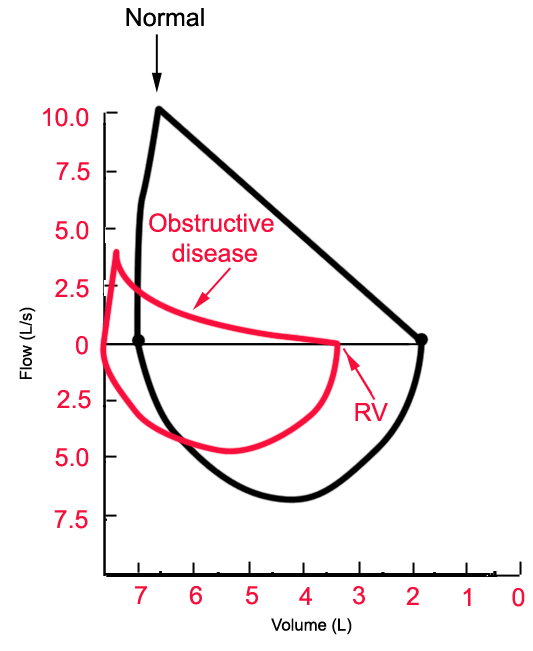
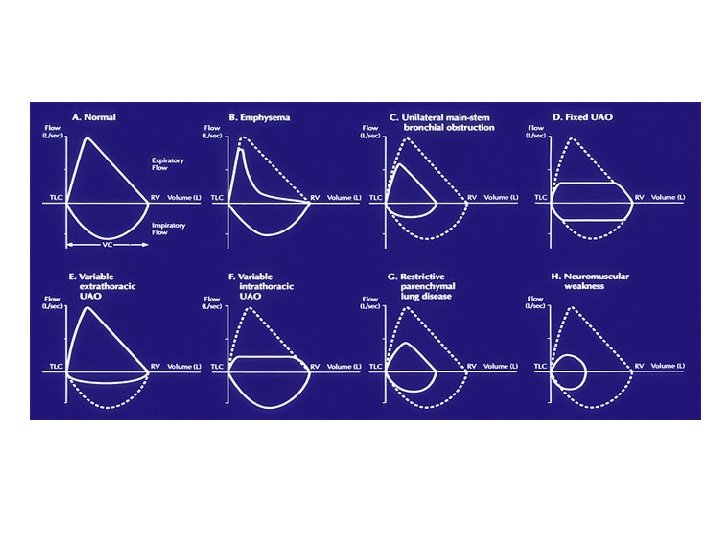
Restrictive lung disease flow volume loop. Nineteen had restrictive disease and 25 had obstructive disease. If FVC is not reduced less than 80 of predicted check FEV1FVC 07 obstructive Is it reversible asthma Not reversible COPD 4. Analyzing flow volume loops provides a quick way to detect lung disease.
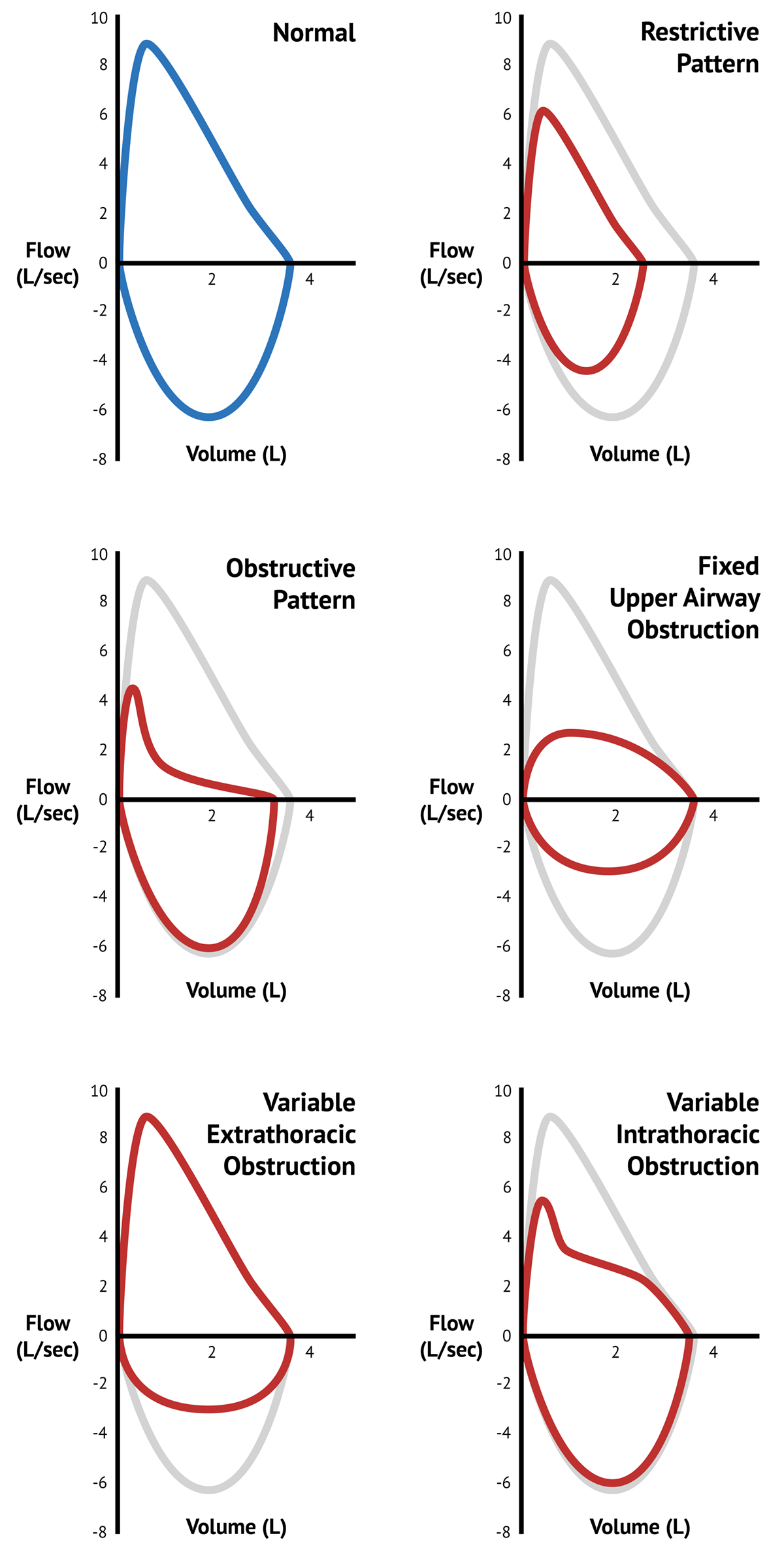
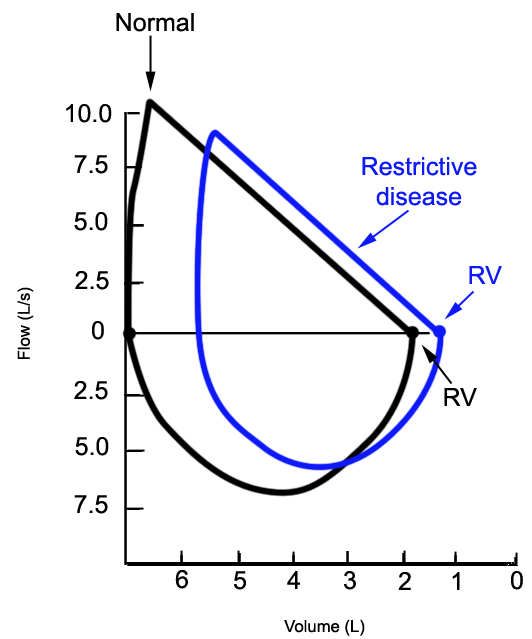
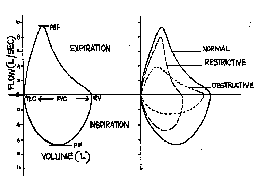
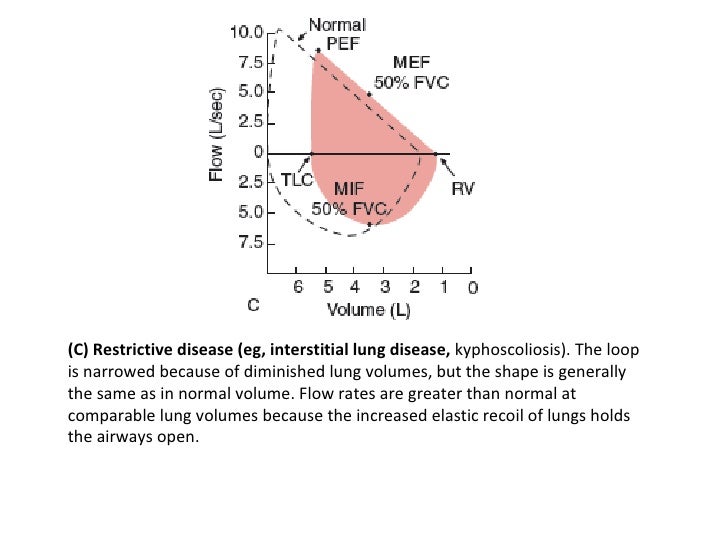
In restrictive lung diseases the shape of the flow volume loop is relatively unaffected but the overall size of the curve will appear smaller when compared to normal on the same scale. Severity of obstructive and restrictive lung disorders. Low tidal volume Rapid decrease in inspiratory flow Rapid expiratory flow with a high peak expiratory flow rate as the inelastic lung recoils.
Peak Expiratory Flow and FEV1 can be normal in restrictive lung disease but are often low as well. An individual with restrictive lung disease can have a normal looking flow-volume loop that is just reduced in overall size. Lung volume after maximal inspiratory effort.
Flow rates are greater than normal at comparable lung volumes because the increased elastic recoil of lungs holds the airways open. The loop is narrowed because of diminished lung volumes but the shape is generally the same as in normal volume. Here plots show maximal inspiration and expiration.
Both Tiffeneau and FVC are too low. A spirometry form a patient with mixed lung disease shows both signs of obstructive and restrictive lung disease. Check that FEV1FVC is normal 07 Restrictive or normal 3.
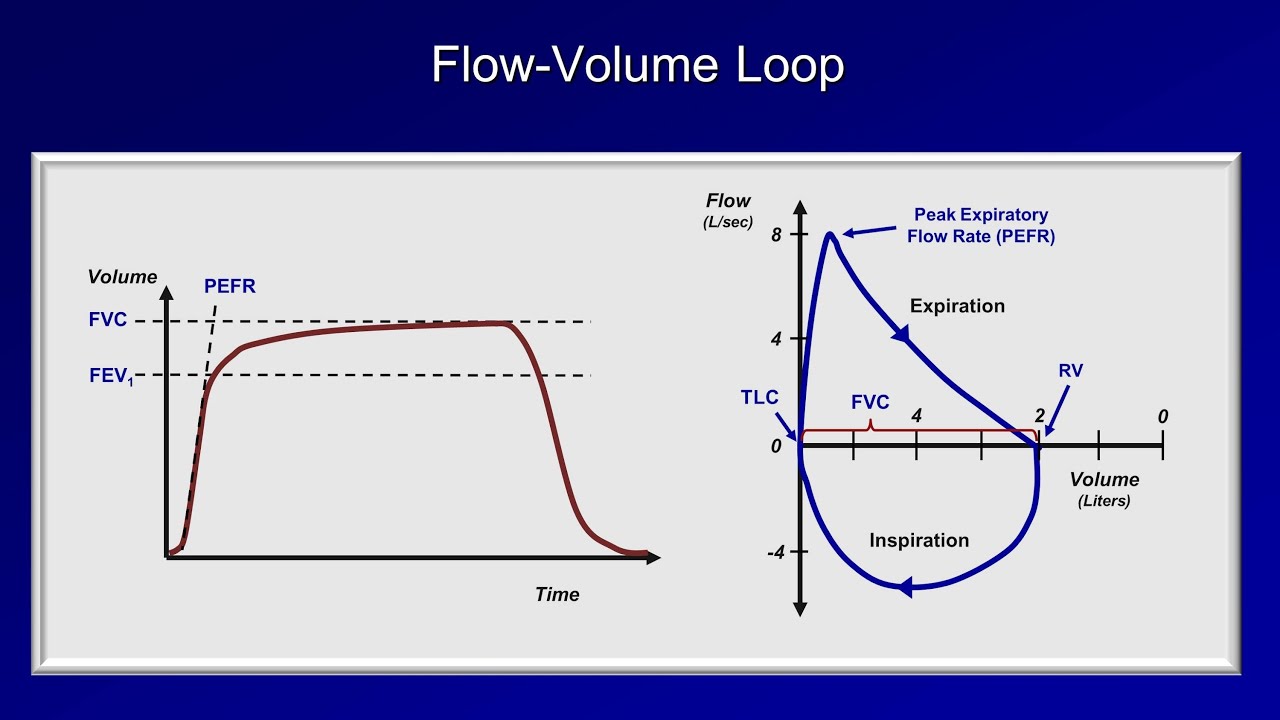
A flow-volume loop plots both inspiration and expiration on the y-axis while flow rate is plotted on the x-axis. The curve assumes a. Thirty-eight were normal smokers and nonsmokers.
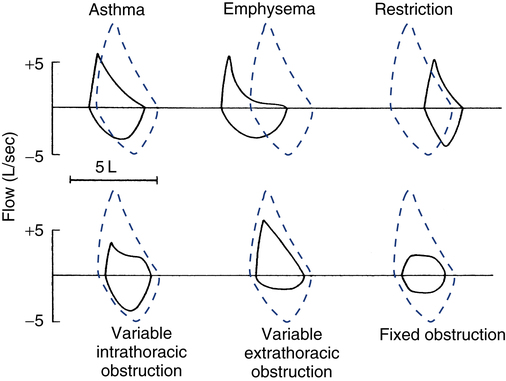
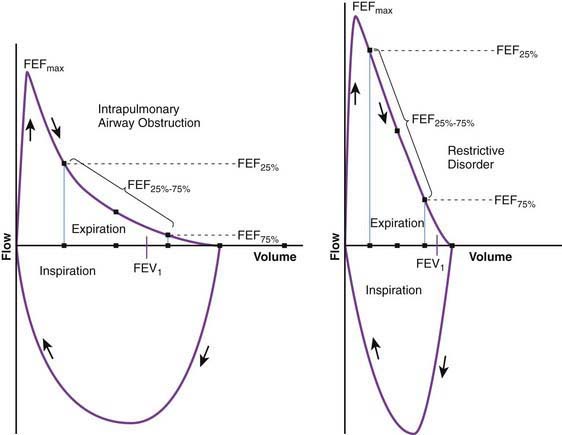
The shape of the flow-volume loop can indicate the location of airflow limitation such as the. Flow volume loops.
The appearance of the loop can reveal the presence of obstructive andor restrictive lung disease.
The Flow-Volume Loop in Normal Subjects and in Diffuse Lung Disease The maximum effort flow-volume MFV loops of 82 subjects were analyzed along with standard spirometric measurements. Flow volume loops. The appearance of the loop can reveal the presence of obstructive andor restrictive lung disease. The shape of the flow-volume loop can indicate the location of airflow limitation such as the. Severity of obstructive and restrictive lung disorders. The curve assumes a. Restrictive and obstructive diseases can co-exist 5. A spirometry form a patient with mixed lung disease shows both signs of obstructive and restrictive lung disease. With these pathologies the flow volume loop is flattened.
The appearance of the loop can reveal the presence of obstructive andor restrictive lung disease. Analyzing flow volume loops provides a quick way to detect lung disease. A relatively symmetrical saddle-shaped curve that runs from the residual volume to the total lung capacity below the x-axis. Obstructive lung disease restrictive lung disease mixed lung disease and upper airway obstructions. Nineteen had restrictive disease and 25 had obstructive disease. Measurements are typically reported as absolute flows and volumes and as percentages of predicted values using data derived. With these pathologies the flow volume loop is flattened.

































Post a Comment for "Restrictive Lung Disease Flow Volume Loop"