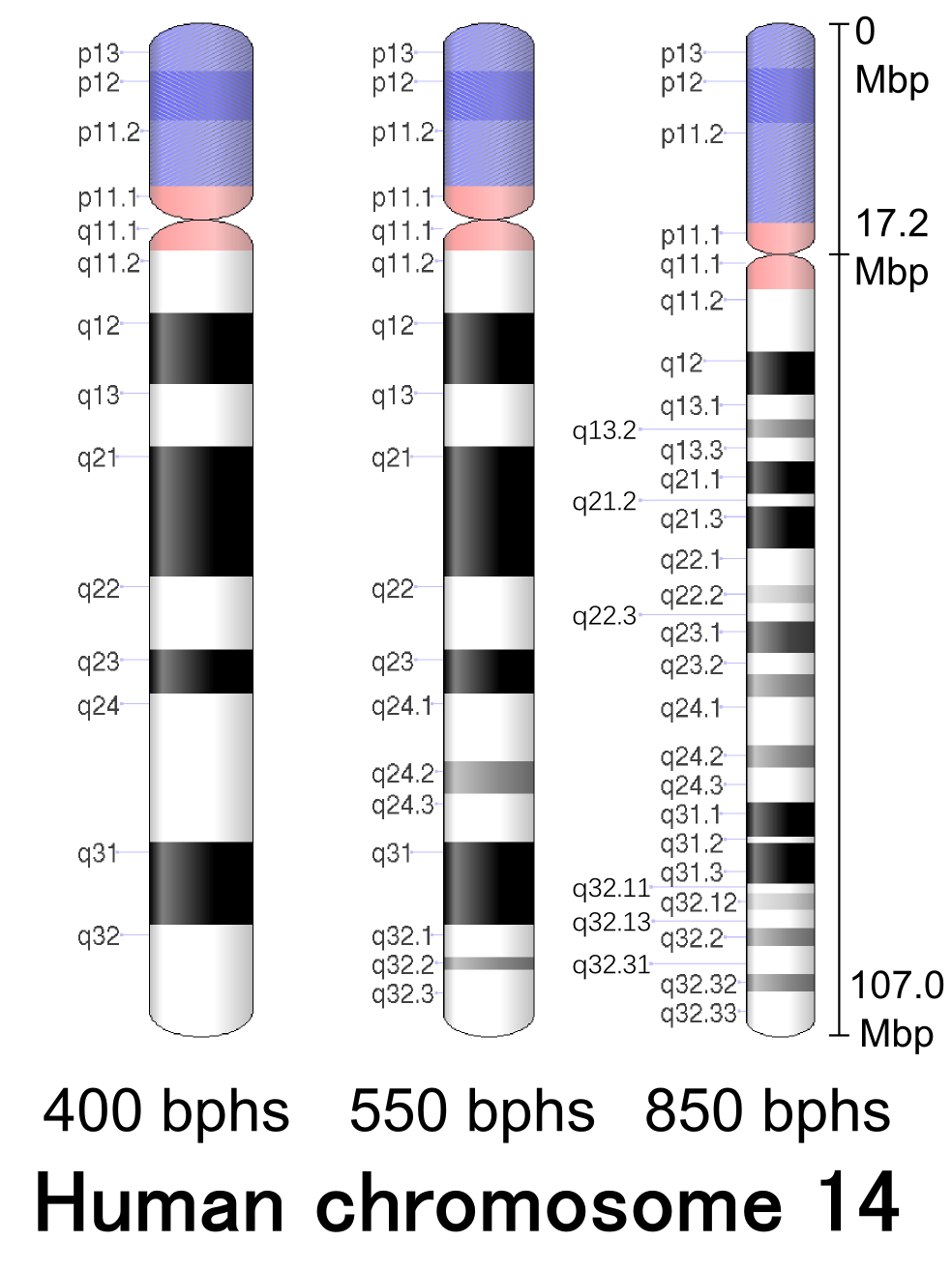
Chromosome 14 Deletion Syndrome
Chromosome 14 deletion syndrome. Recurrent seizures epilepsy develop in infancy or early childhood. A deletion of genetic material from part of the long q arm of chromosome 14 can cause FOXG1 syndrome which is a rare disorder characterized by impaired development and structural brain abnormalities. Affected infants and children typically have delays in the acquisition of skills that require the coordination of physical and mental activities psychomotor delays mental retardation growth delays and episodes of uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain seizures.
The causes of chromosomal syndromes. 14- Williams Syndrome. A number sign is used with this entry because it represents a contiguous gene deletion syndrome on chromosome 15q14.
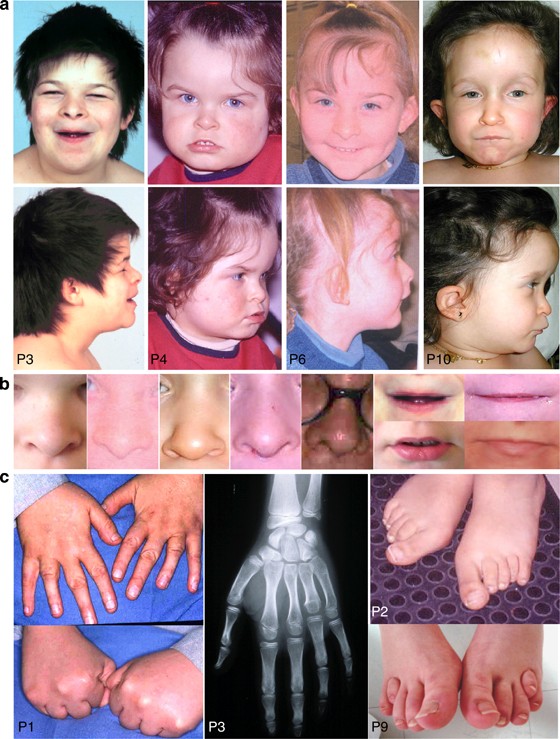
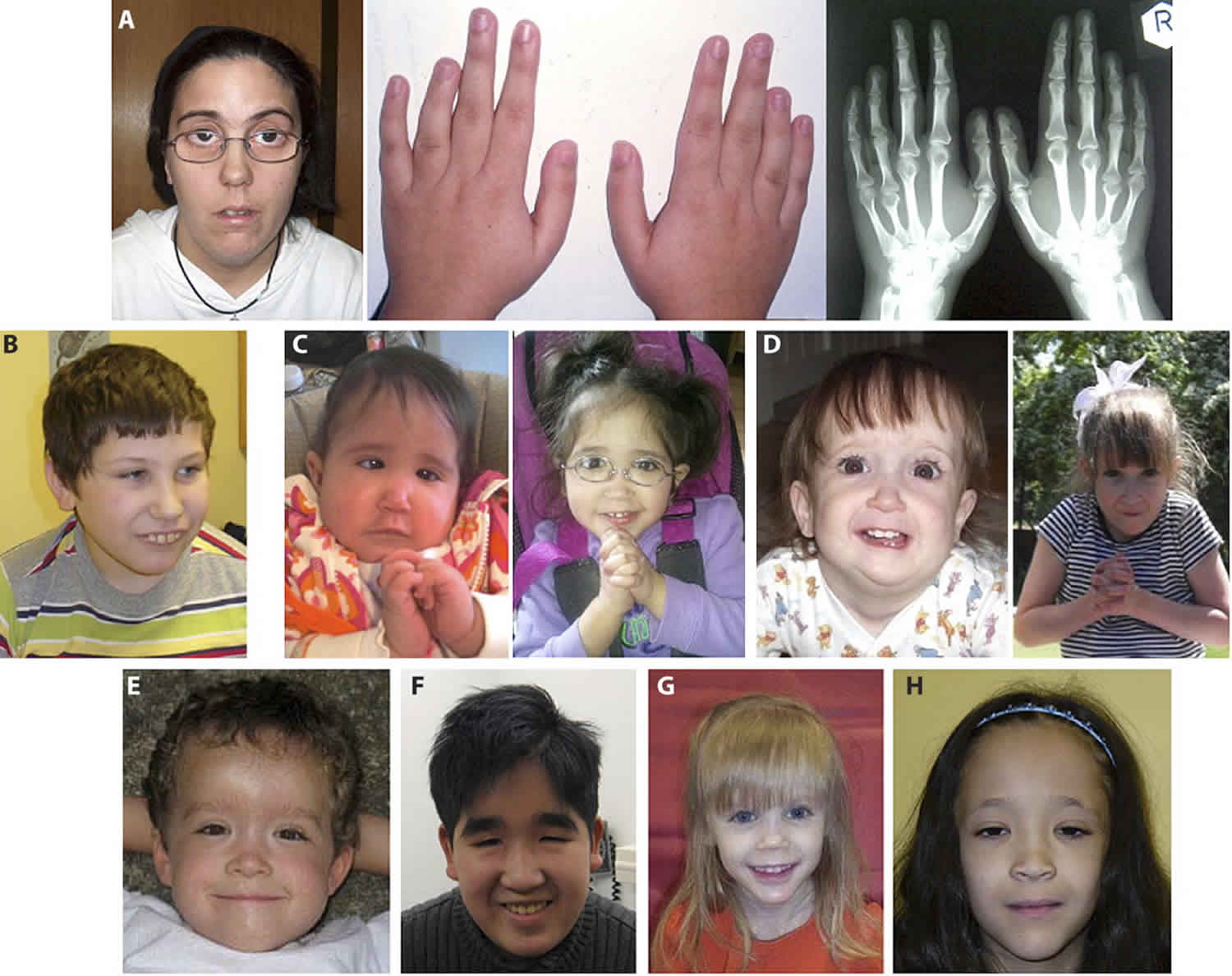
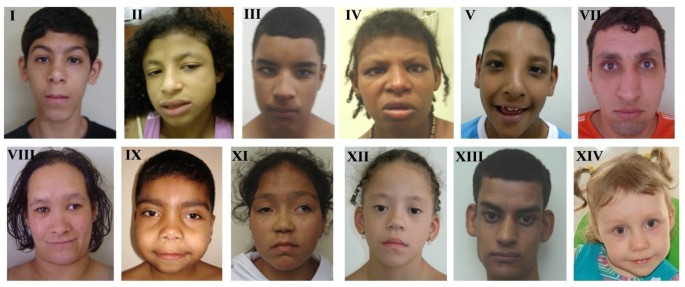
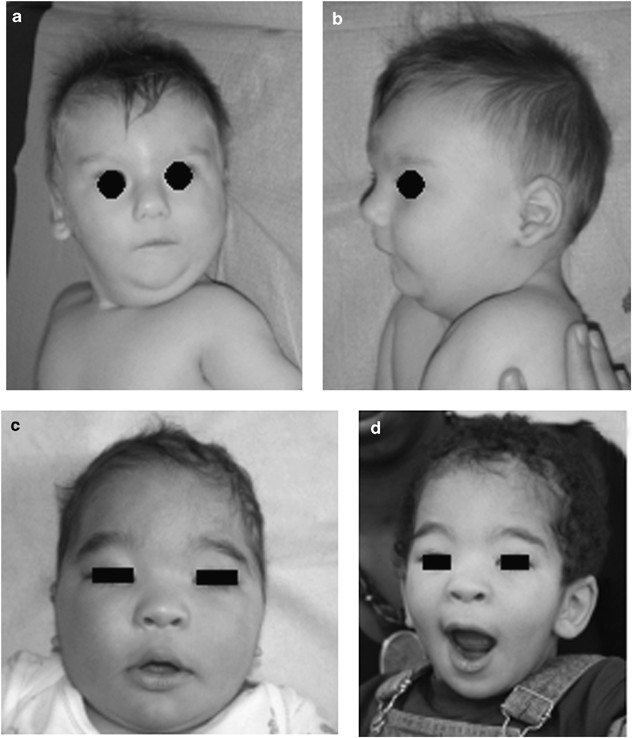
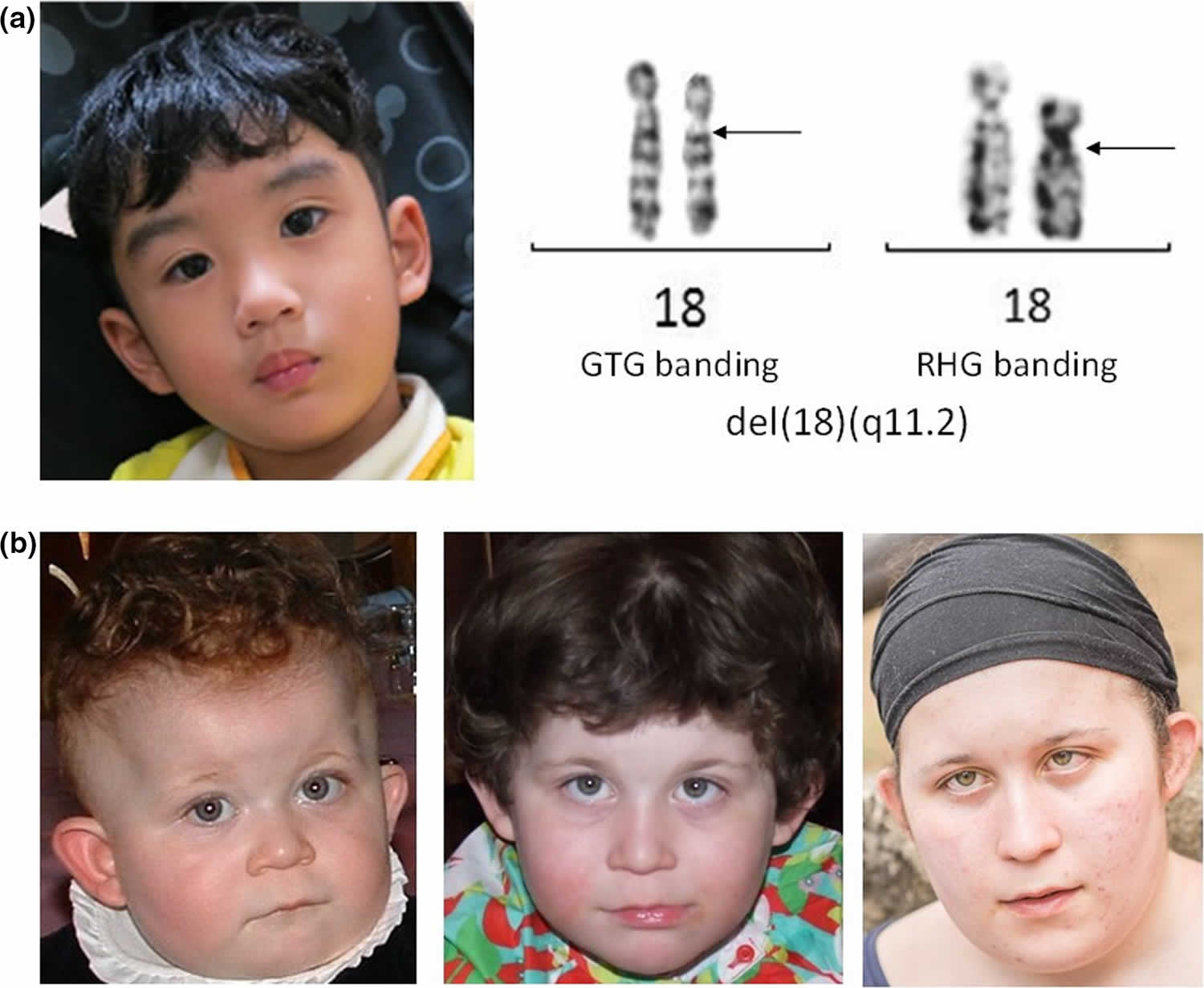
P12-112 Deletion Syndrome can cause unusual facial features developmental delays small head circumference. Recurrent seizures epilepsy develop in infancy or early childhood. Distinctive facial features Developmental delay Intellectual deficiency Behavioral problems.
The signs and symptoms of Chromosome 14q Deletion Syndrome may vary among affected individuals in type and severity and include. 41 filas 5q143 microdeletion syndrome is characterized by severe intellectual. Genetic and epigenetic abnormalities affecting these imprinted gene clusters result in two different phenotypes currently known as maternal upd14 syndrome and paternal upd14 syndrome.
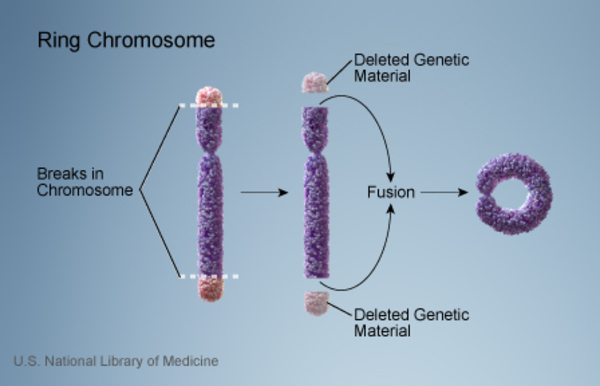
This pathology is characterized by atypical facial alterations cardiovascular problems cognitive delay learning problems etc. It is a congenital disorder. Ring chromosome 14 syndrome R 14 syndrome OMIM 616606 is extremely rare and its prevalence and incidence are unknown.
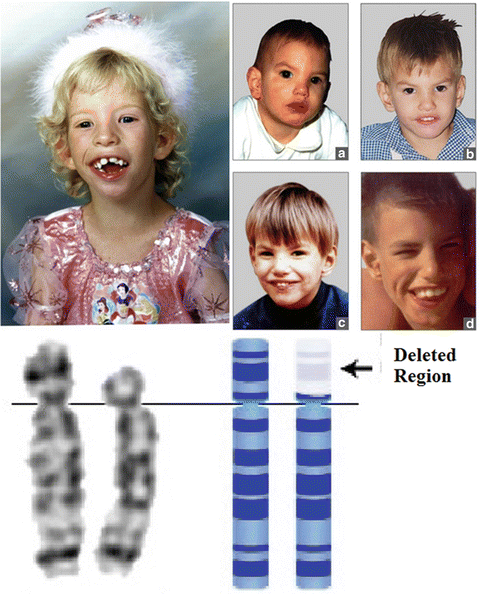
The deleted region includes the MEIS2 gene 601740. In many cases the seizures are resistant to treatment with anti-epileptic drugs. However only few patients carrying a maternal deletion at the 14q322-imprinted critical.
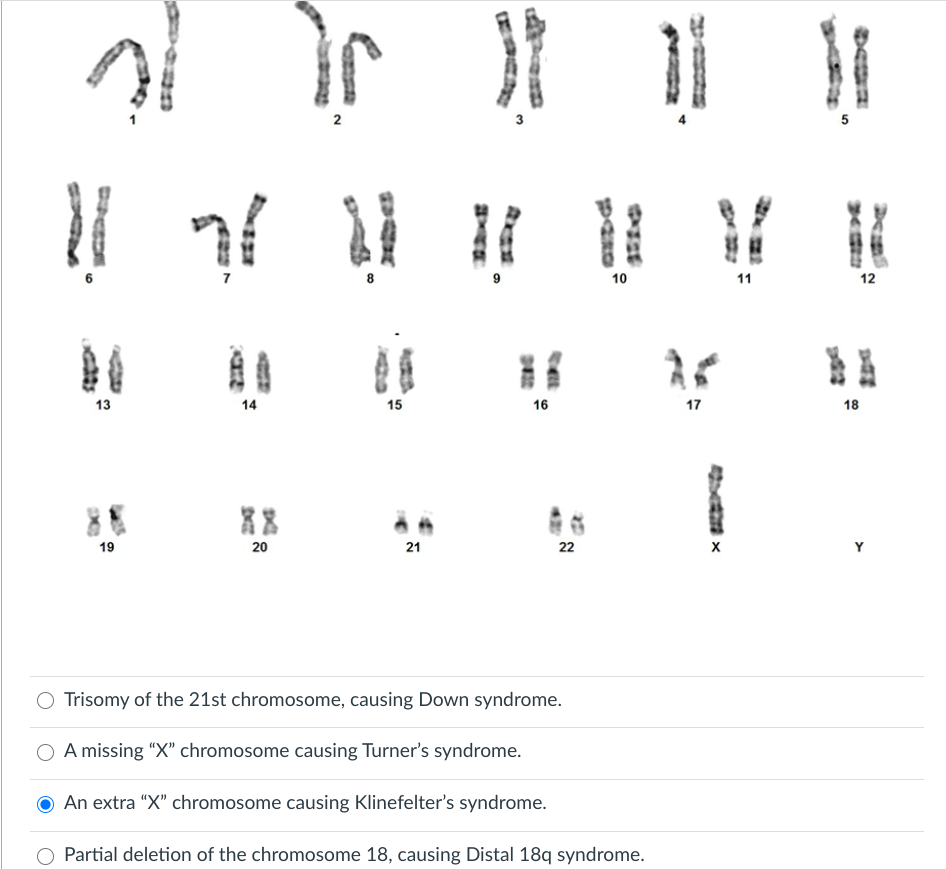
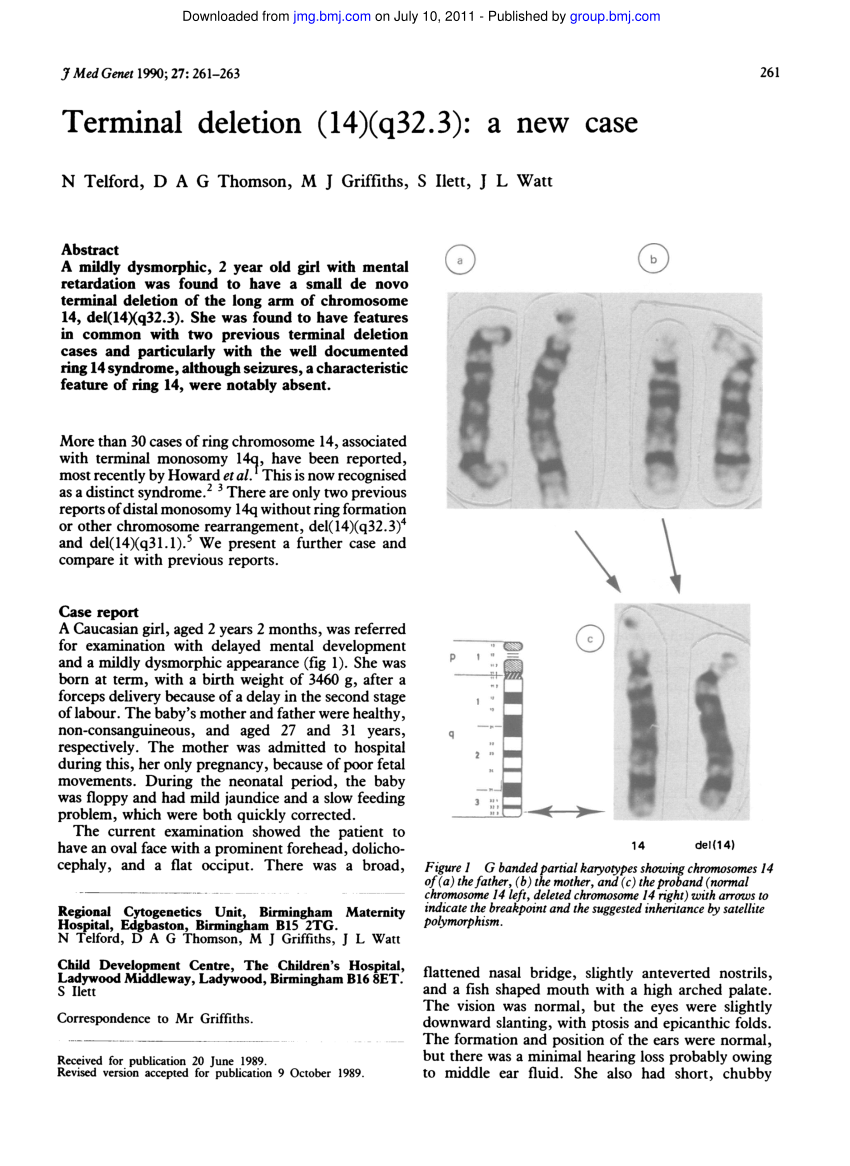
To date over 80 cases have been described since the first report in 1971 8. The deletion may range from 5 million to 16 million deleted DNA base pairs.
In many cases the seizures are resistant to treatment with anti-epileptic drugs.
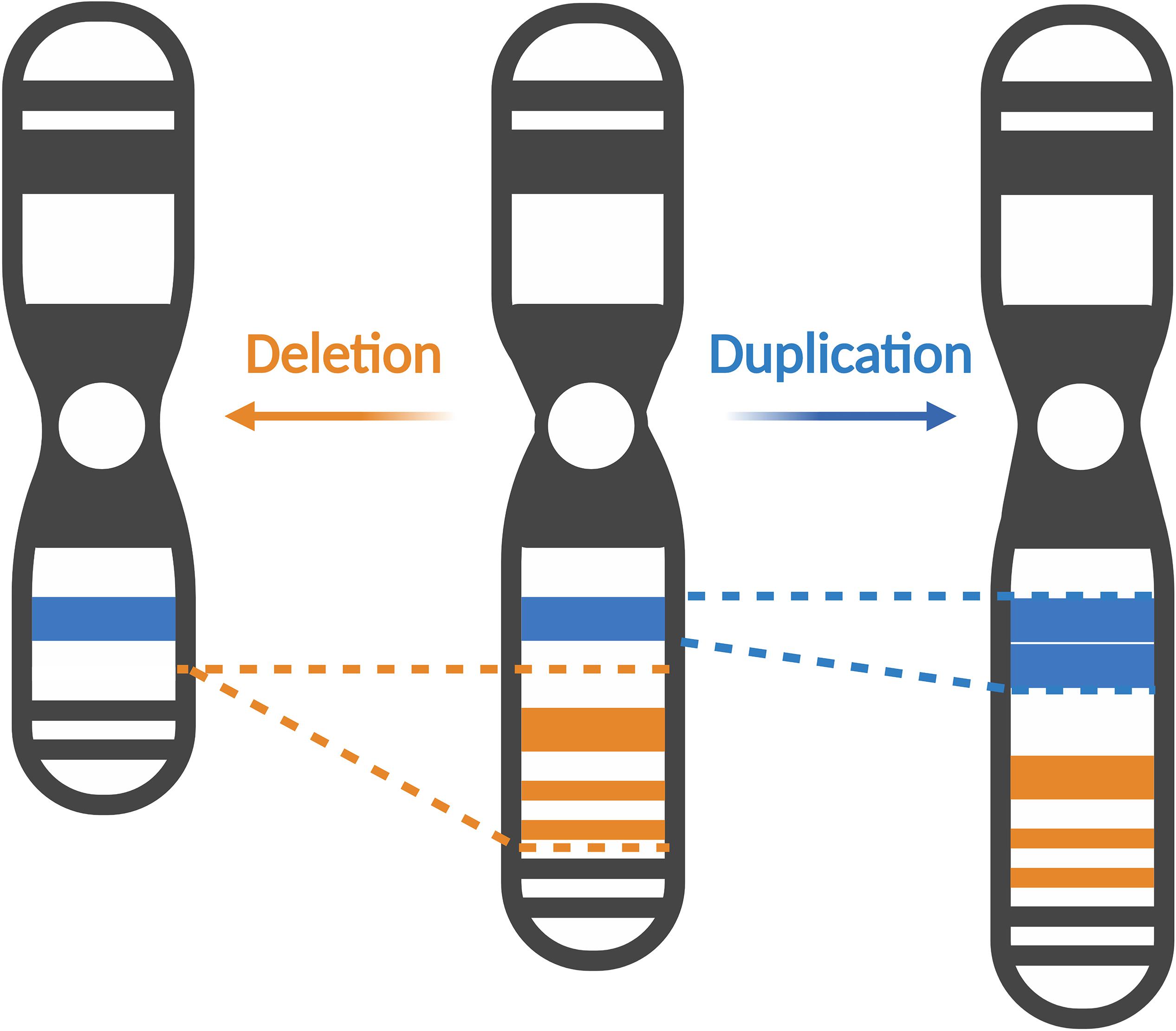
14- Williams Syndrome. The deleted region includes the MEIS2 gene 601740. Chromosome 14q deletion is a chromosome abnormality that occurs when there is a missing deleted copy of genetic material on the long arm q of chromosome 14. Recurrent seizures epilepsy develop in infancy or early childhood. 41 filas 5q143 microdeletion syndrome is characterized by severe intellectual. The causes of chromosomal syndromes. If the material that has been deleted contains important genes developmental delay learning disability and health problems may occur. Since the deletion takes place on the q arm of chromosome 11 it is also called 11q terminal deletion disorder. The signs and symptoms of Chromosome 14q Deletion Syndrome may vary among affected individuals in type and severity and include.
A number sign is used with this entry because it represents a contiguous gene deletion syndrome on chromosome 15q14. Deletions of Chromosome 14 Chromosome 14 as well as chromosome 13 is an acrocentric chromosome. Genetic and epigenetic abnormalities affecting these imprinted gene clusters result in two different phenotypes currently known as maternal upd14 syndrome and paternal upd14 syndrome. Loss or duplication of the short arm of this chromosome does not lead to any clinical abnormalities. A deletion of genetic material from part of the long q arm of chromosome 14 can cause FOXG1 syndrome which is a rare disorder characterized by impaired development and structural brain abnormalities. Ring chromosome 14 syndrome is a condition characterized by seizures and intellectual disability. Recurrent seizures epilepsy develop in infancy or early childhood.


























Post a Comment for "Chromosome 14 Deletion Syndrome"